Information - Pressure tanks - hydrophore tanks
Pre-charge pressure of pressure tank
Pre-charge pressure of pressure tank
Author Akvedukts
In water supply systems, the pressure tank (also called hydrophore tank, hydraulic accumulator, bladder autoclave, hydro accumulator, hydrophore) is used to equalize pressure, prevent hydraulic shock, ensure uninterrupted operation of pumps. Read more about hydro accumulators, their different names and types in this article. Pre-charge pressure of the pressure tank means the counterpressure of the air in this tank. This article tells about pre-charge pressure adjustment and checking.
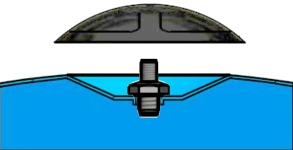
Air valve (Schrader valve) of pressure tank
The pressure tank air valve is the same as for bicycle and car tires, so you can use the same tools that are used for tire pressure - an air pressure gauge and a hand pump or compressor with an appropriate nozzle to control and provide pre-charge pressure in the pressure tank. The air valve is located on the side of the pressure tank opposite the water connection, under the plastic protective cover (see figure).
Pre-charge pressure or pressure of air in the pressure tank
Air, which, unlike water, is compressible and changes its volume depending on pressure - it is used to absorb and dampen hydraulic vibrations. This is according to Boyle's law, which states that the multiplication of pressure and volume before they change is equal to the multiplication of pressure and volume after they change, i.e., when pressure increases, volume decreases, and vice versa.
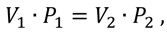
Where
V1 - volume of gas in a closed vessel before the change in pressure and volume,
P1 - pressure of gas in a closed vessel before the change in pressure and volume,
V2 - volume of gas in a closed vessel after the change of pressure and volume,
P2 - gas pressure in a closed vessel after the change in pressure and volume.
Once you understand this law, you can understand how the volume of water and air in the pressure tank varies with changes in pressure in the water system, and why the amount of water in the pressure tank will never equal the volume of the tank itself if air is pumped into it.
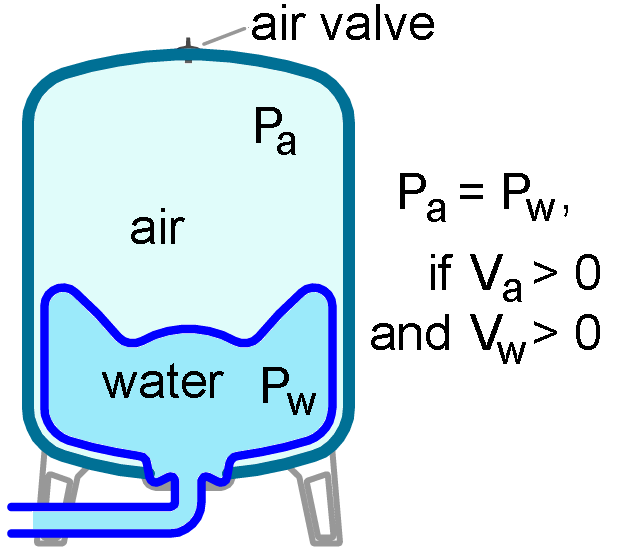
The second important point to remember is that if the volume of water and air ( Vw and Va ) in the pressure tank is greater than 0, then the pressure on both sides of the diaphragm ( Pw and Pa ) is always the same. This means that the pre-charge pressure (air pressure) in the pressure tank cannot be measured if there is water from the water supply system in the pressure tank. In that case, when the air pressure is measured, it will be almost equal to the current pressure in the system of water supply. The pre-charge pressure of the air must be 0.2 bar below the minimum pressure in the water supply, so in a properly functioning system a certain amount of water will always be pressurized into the pressure tank. If there is a loss of pre-charge pressure in the tank due to any leakage, pump operation will be impaired and the rubber diaphragm will be mechanically damaged.
Checking and adjusting the pre-charge pressure of the pressure tank
The pre-charge pressure of the pressure tank must be 0.2 bar less than the pump start pressure. At the factory a certain pre-charge pressure is pumped into tank, and is indicated on the pressure tank's data plate (usually 1.5 bar). The first time the pre-charge pressure should be checked when the pump is installed and, if necessary, raised or lowered according to the required water pump start pressure. From then on, check the pre-charge pressure every 6 to 12 months or if pre-charge pressure loss is suspected. Knowing the theory described in the previous chapter, you can understandably proceed to check the pre-charge pressure in the pressure tank, which can be done in the following steps:
1) get access to the pressure tank air valve and press it for a moment; if air without water is squeezed out of the valve, proceed as described below; if water is squeezed out of the valve together with air, the pressure tank bladder must be replaced (see here) and then proceed as described in paragraphs 2 to 7 on pre-charge pressure; if air does not come out at all when the valve is pressed, continue with the steps below, but note that there may be damage to the bladder, air valve, or walls of the pressure tank
2) Disconnect the pump from the power supply, close the valves on both sides of the pump (if fitted)
3) One of the water taps on the system must be open so that excess water can drain out of the water supply system and it is not under pressure; only in this situation you can be sure that the pre-charge pressure in the pressure tank is measured and not that of the water supply system
4) Measure the air pressure in the tank with a car tire pressure gauge, it should be 0.2 bar less than the pump start pressure.
5) If the pressure is insufficient, inflate it to the necessary value using a bicycle or car tire pump; if during the check performed in the first step no air came out of the valve at all, after pumping the air, check if water comes out with the air; if no water comes with air and air pressure in the tank cannot be increased to the necessary value, the cause of the air loss is the leakiness of the tank walls and it is necessary to change the tank.
6) If air pressure is raised to the proper value and no problems are found that would indicate air leakage in the diaphragm, tank wall, or valve, the pre-charge pressure test can be considered successfully completed.
7) Close the opened water tap, open the closed valves before and after the pump, connect the pump to power supply and turn it on.


